Thailand Reports Asia’s First Case of New Deadlier Mpox Variant
Thailand has confirmed the first case of a new deadly strain of the mpox virus in Asia. The confirmed patient is a 66-year-old European person, he has tested positive for the virus after arriving in Bangkok on August 14. According to the report before arriving in Thailand the patient had traveled from Africa to the United Kingdom.
The Department of Disease Control in Thailand confirmed that the man was infected with the Mpox Clade 1b strain after multiple lab tests. “Thailand’s Department of Disease Control confirms the presence of mpox Clade 1b in a European patient,” stated the department in an official release.
Authorities have identified 43 individuals who had close contact with the patient. While none have shown symptoms thus far, they will continue to be monitored for 21 days to ensure no further spread of the virus.
Since 2022, Thailand has reported 800 cases of Mpox Clade 2, marking this latest case as a significant development in the region’s public health landscape.
Precautionary Measures in India
As of now, no cases of Mpox have been reported in India. However, the All-India Institute for Medical Sciences (AIIMS) has issued protocols for handling suspected cases, and government hospitals in Delhi have been directed to establish isolation rooms for potential patients.
Additionally, authorities at airports, ports, and borders with Bangladesh and Pakistan have been instructed to remain vigilant and screen passengers for symptoms of the virus.
Know more about MPOX:
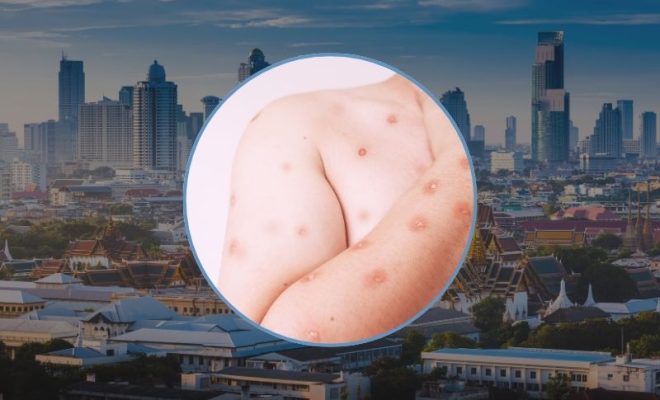
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines Mpox as an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus. It is characterized by a painful rash, swollen lymph nodes, and fever. While most individuals recover fully, some may experience severe illness.
WHO shared details about MPOX on its official X handle:
Transmission and Prevention
Mpox spreads among humans through direct contact, kissing, or sexual activity. Pregnant individuals diagnosed with the virus may also transmit it to their unborn children. Those with compromised immune systems, such as HIV patients, are at higher risk of complications from the virus.
WHO introduced prevention measures in its official X handle, that includes avoiding physical contact with infected individuals and vaccination for those at risk.



